Prediction of Confidence Rating and Reaction Time Distribution in the drift diffusion confidence model
Source:R/predictratingdist_DDConf.R
predictDDConf.RdpredictDDConf_Conf predicts the categorical response distribution of
decision and confidence ratings, predictDDConf_RT computes the
RT distribution (density) in the drift diffusion confidence model
(Hellmann et al., 2023), given specific parameter
constellations. See dDDConf for more information about the model
and parameters.
Usage
predictDDConf_Conf(paramDf, maxrt = Inf, subdivisions = 100L,
stop.on.error = FALSE, .progress = TRUE)
predictDDConf_RT(paramDf, maxrt = 9, subdivisions = 100L, minrt = NULL,
scaled = FALSE, DistConf = NULL, .progress = TRUE)Arguments
- paramDf
a list or data frame with one row. Column names should match the names of DDConf model parameter names. For different stimulus quality/mean drift rates, names should be
v1,v2,v3,.... Differentsvand/orsparameters are possible withsv1,sv2,sv3... (s1,s2,s3,... respectively) with equally many steps as for drift rates. Additionally, the confidence thresholds should be given by names withthetaUpper1,thetaUpper2,...,thetaLower1,... or, for symmetric thresholds only bytheta1,theta2,....- maxrt
numeric. The maximum RT for the integration/density computation. Default: 15 (for
predictDDConf_Conf(integration)), 9 (forpredictDDConf_RT).- subdivisions
integer(default: 100). ForpredictDDConf_Confit is used as argument for the inner integral routine. ForpredictDDConf_RTit is the number of points for which the density is computed.- stop.on.error
logical. Argument directly passed on to integrate. Default is
FALSE, since the densities invoked may lead to slow convergence of the integrals (which are still quite accurate) which causes R to throw an error.- .progress
logical. If
TRUE(default) a progress bar is drawn to the console.- minrt
numeric or
NULL(default). The minimum rt for the density computation.- scaled
logical. For
predictDDConf_RT. Whether the computed density should be scaled to integrate to one (additional columndensscaled). Otherwise the output contains only the defective density (i.e. its integral is equal to the probability of a response and not 1). IfTRUE, the argumentDistConfshould be given, if available. Default:FALSE.- DistConf
NULLordata.frame. Adata.frameormatrixwith column names, giving the distribution of response and rating choices for different conditions and stimulus categories in the form of the output ofpredictDDConf_Conf. It is only necessary, ifscaled=TRUE, because these probabilities are used for scaling. Ifscaled=TRUEandDistConf=NULL, it will be computed with the functionpredictDDConf_Conf, which takes some time and the function will throw a message. Default:NULL
Value
predictDDConf_Conf returns a data.frame/tibble with columns: condition, stimulus,
response, rating, correct, p, info, err. p is the predicted probability of a response
and rating, given the stimulus category and condition. info and err refer to the
respective outputs of the integration routine used for the computation.
predictDDConf_RT returns a data.frame/tibble with columns: condition, stimulus,
response, rating, correct, rt and dens (and densscaled, if scaled=TRUE).
Details
The function predictDDConf_Conf consists merely of an integration of
the response time density, dDDConf, over the
response time in a reasonable interval (0 to maxrt). The function
predictDDConf_RT wraps these density
functions to a parameter set input and a data.frame output.
For the argument paramDf, the output of the fitting function fitRTConf
with the DDConf model may be used.
Note
Different parameters for different conditions are only allowed for drift rate
v, drift rate variability sv, and process variability s. Otherwise, s is
not required in paramDf but set to 1 by default. All other parameters are used for all
conditions.
References
Hellmann, S., Zehetleitner, M., & Rausch, M. (2023). Simultaneous modeling of choice, confidence and response time in visual perception. Psychological Review 2023 Mar 13. doi: 10.1037/rev0000411. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36913292.
Examples
# 1. Define some parameter set in a data.frame
paramDf <- data.frame(a=2,v1=0.5, v2=1, t0=0.1,z=0.55,
sz=0,sv=0.2, st0=0, theta1=0.8)
# 2. Predict discrete Choice x Confidence distribution:
preds_Conf <- predictDDConf_Conf(paramDf, maxrt = 15)
head(preds_Conf)
#> condition stimulus response correct rating p info err
#> 1 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.32260885 OK 9.980641e-06
#> 2 2 -1 -1 1 1 0.32597348 OK 2.002264e-05
#> 3 1 1 -1 0 1 0.11438204 OK 3.269940e-06
#> 4 2 1 -1 0 1 0.04054175 OK 2.148754e-06
#> 5 1 -1 1 1 1 0.12691602 OK 1.552460e-06
#> 6 2 -1 1 1 1 0.04961359 OK 6.704916e-07
# 3. Compute RT density
preds_RT <- predictDDConf_RT(paramDf, maxrt=4, subdivisions=200) #(scaled=FALSE)
# same output with scaled density column:
preds_RT <- predictDDConf_RT(paramDf, maxrt=4, subdivisions=200,
scaled=TRUE, DistConf = preds_Conf)
head(preds_RT)
#> condition stimulus response correct rating rt dens densscaled
#> 1 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1000000 0 0
#> 2 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1195980 0 0
#> 3 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1391960 0 0
#> 4 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1587940 0 0
#> 5 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1783920 0 0
#> 6 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1979899 0 0
# \donttest{
# Example of visualization
library(ggplot2)
preds_Conf$rating <- factor(preds_Conf$rating, labels=c("unsure", "sure"))
preds_RT$rating <- factor(preds_RT$rating, labels=c("unsure", "sure"))
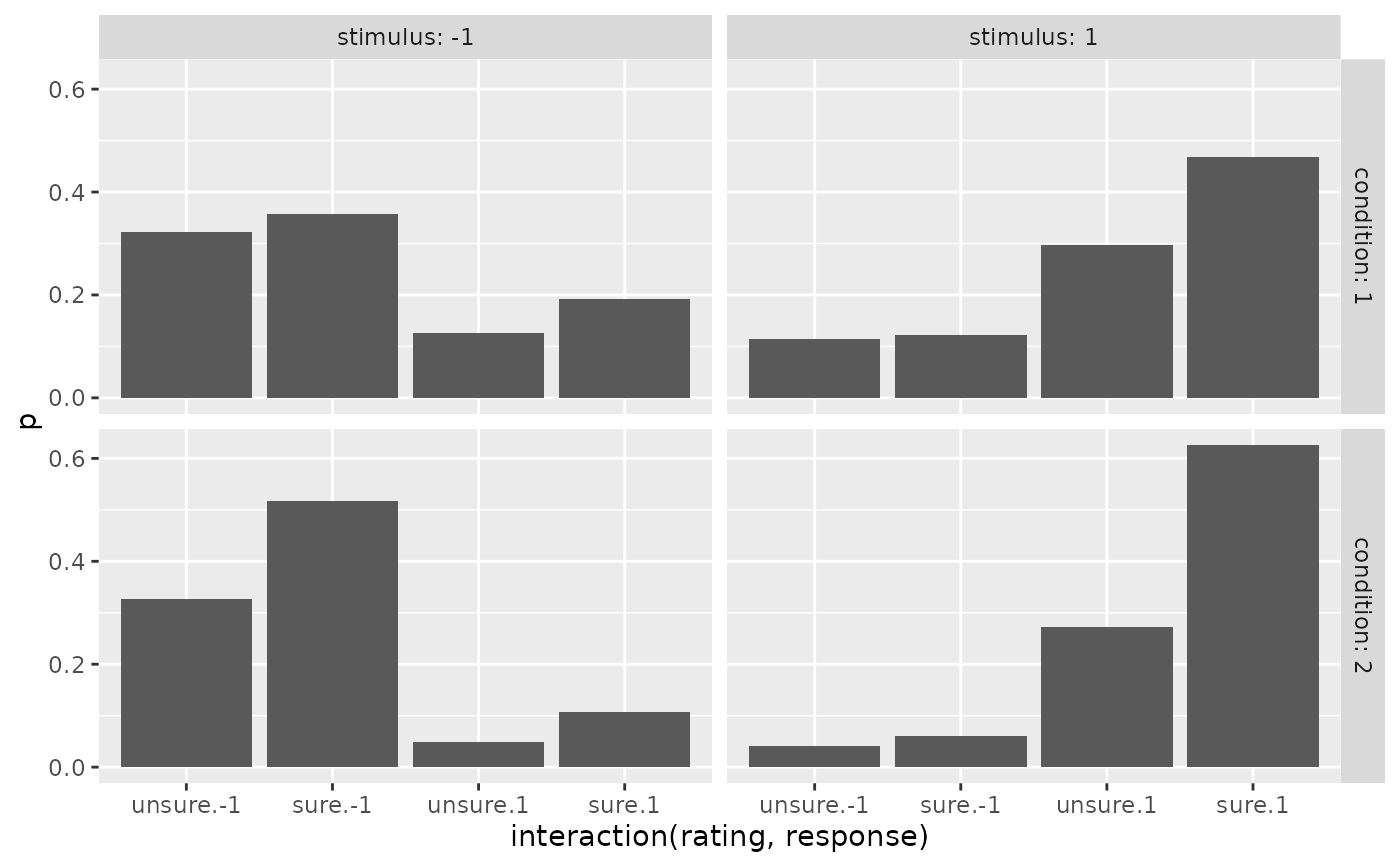
ggplot(preds_Conf, aes(x=interaction(rating, response), y=p))+
geom_bar(stat="identity")+
facet_grid(cols=vars(stimulus), rows=vars(condition), labeller = "label_both")
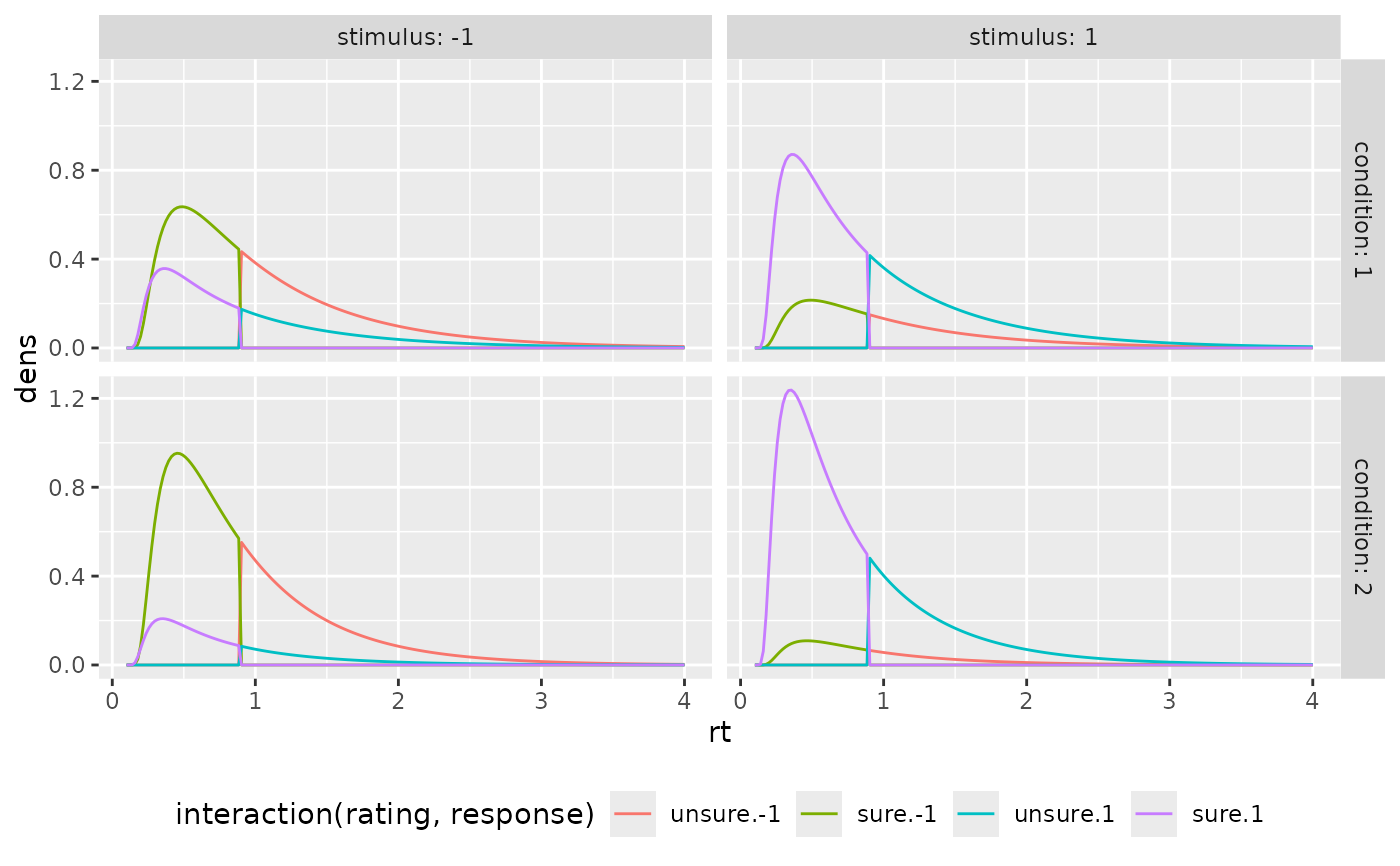
 ggplot(preds_RT, aes(x=rt, color=interaction(rating, response), y=dens))+
geom_line(stat="identity")+
facet_grid(cols=vars(stimulus), rows=vars(condition), labeller = "label_both")+
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
ggplot(preds_RT, aes(x=rt, color=interaction(rating, response), y=dens))+
geom_line(stat="identity")+
facet_grid(cols=vars(stimulus), rows=vars(condition), labeller = "label_both")+
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
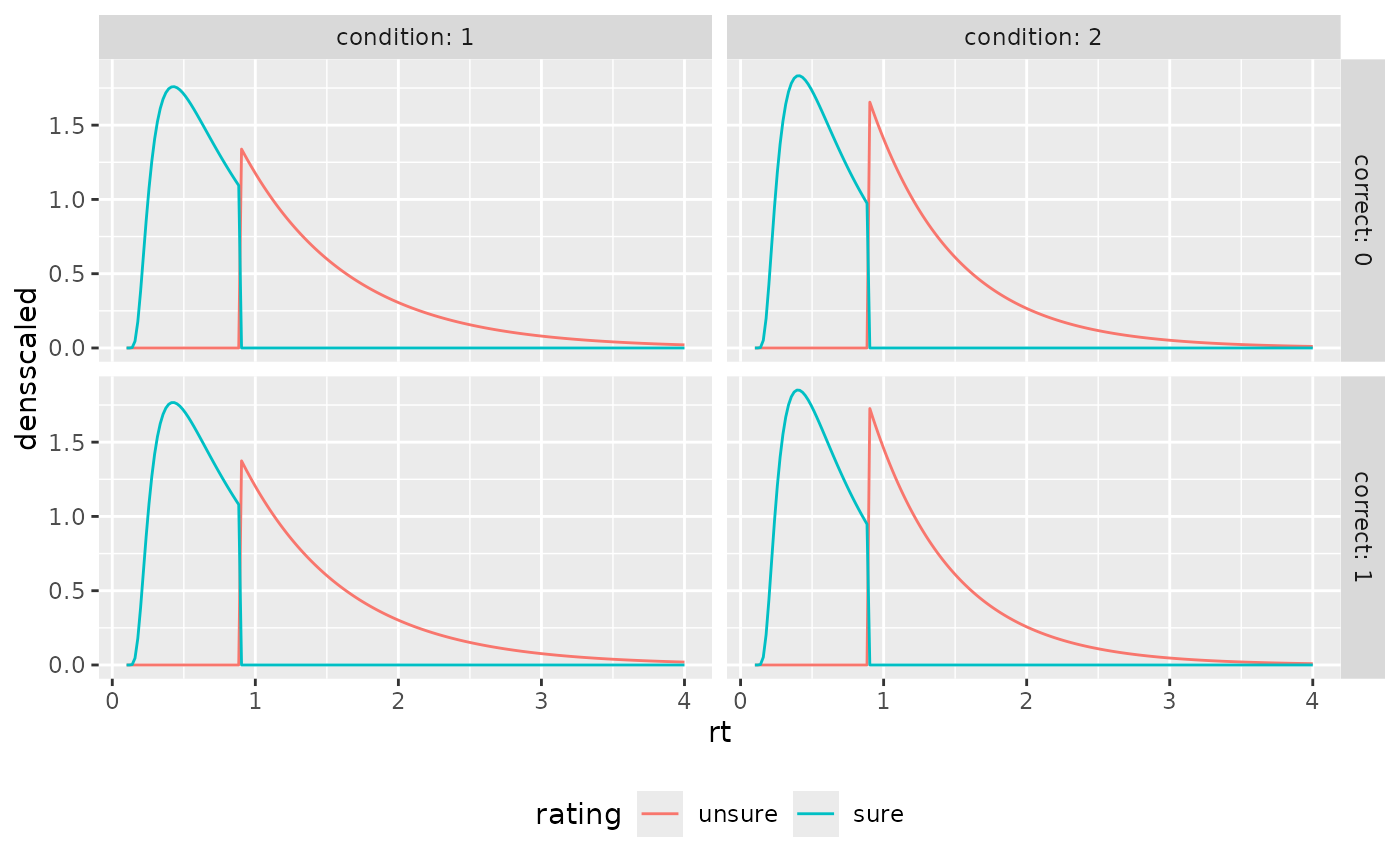
 ggplot(aggregate(densscaled~rt+correct+rating+condition, preds_RT, mean),
aes(x=rt, color=rating, y=densscaled))+
geom_line(stat="identity")+
facet_grid(cols=vars(condition), rows=vars(correct), labeller = "label_both")+
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
ggplot(aggregate(densscaled~rt+correct+rating+condition, preds_RT, mean),
aes(x=rt, color=rating, y=densscaled))+
geom_line(stat="identity")+
facet_grid(cols=vars(condition), rows=vars(correct), labeller = "label_both")+
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
 # }
# Use PDFtoQuantiles to get predicted RT quantiles
head(PDFtoQuantiles(preds_RT, scaled = FALSE))
#> # A tibble: 6 × 7
#> condition stimulus response correct rating p q
#> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.1 0.962
#> 2 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.3 1.16
#> 3 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.5 1.39
#> 4 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.7 1.75
#> 5 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.9 2.49
#> 6 1 -1 -1 1 sure 0.1 0.335
# }
# Use PDFtoQuantiles to get predicted RT quantiles
head(PDFtoQuantiles(preds_RT, scaled = FALSE))
#> # A tibble: 6 × 7
#> condition stimulus response correct rating p q
#> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.1 0.962
#> 2 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.3 1.16
#> 3 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.5 1.39
#> 4 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.7 1.75
#> 5 1 -1 -1 1 unsure 0.9 2.49
#> 6 1 -1 -1 1 sure 0.1 0.335